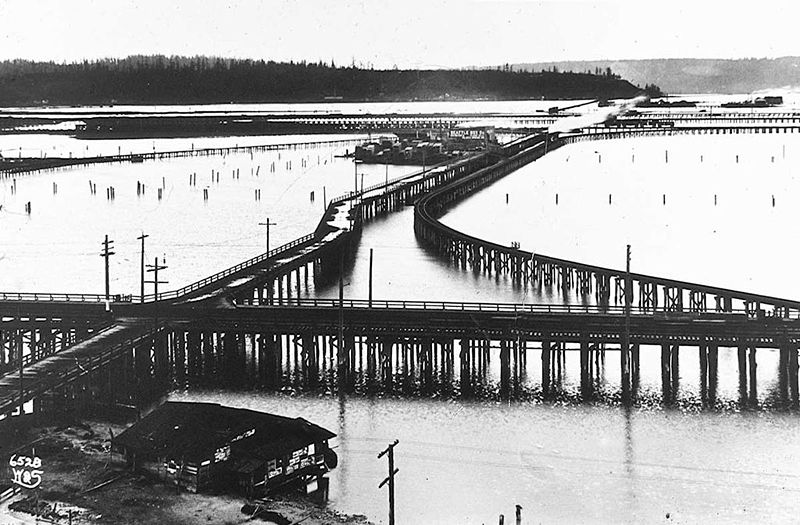
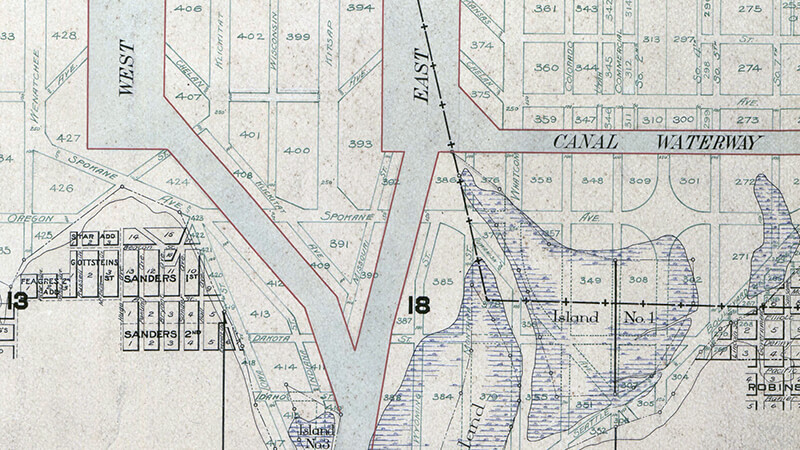
As part of the Great Renaming of 1895, Texas Street, Town Street, Fontenelle Street, Flemming Street, Davidson Street, and Canal Street became Atlantic Street, from Elliott Bay to Lake Washington. The name was extended into West Seattle in 1907, when Grant Street and Louisiana Street were combined.

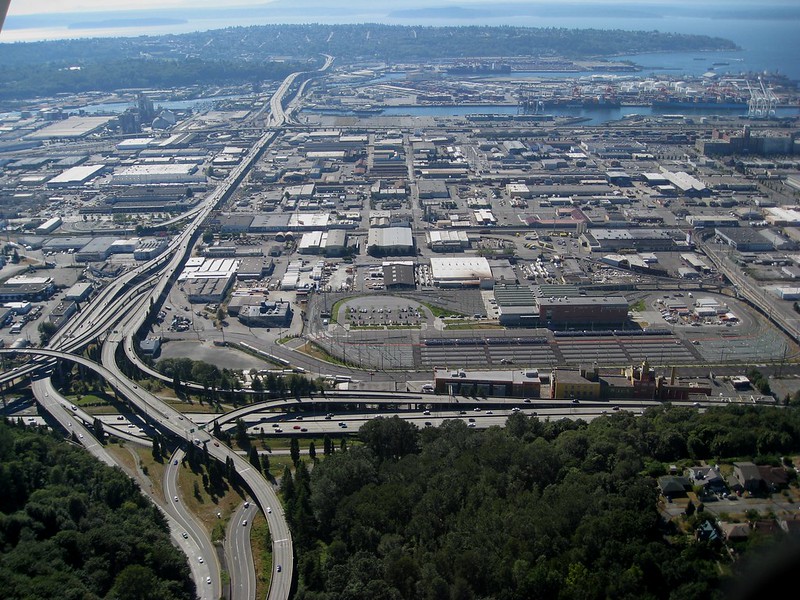
Today, SW Atlantic Street begins in West Seattle at Sunset Avenue SW and goes ¼ of a mile east to Palm Avenue SW. It next appears, as S Atlantic Street, just east of U.S. Coast Guard Base Seattle at Alaskan Way S, and goes around 800 feet east to 1st Avenue S, where it becomes Edgar Martinez Drive S (renamed in honor of the ball player in 2004). Apart from a stub east of Airport Way S that is soon blocked by Interstate 5, the street’s next appearance is on Beacon Hill, where it goes ⅓ of a mile from just west of 11th Avenue S to 17th Avenue S, the portion between 15th Avenue S and 16th Avenue S being a stairway.
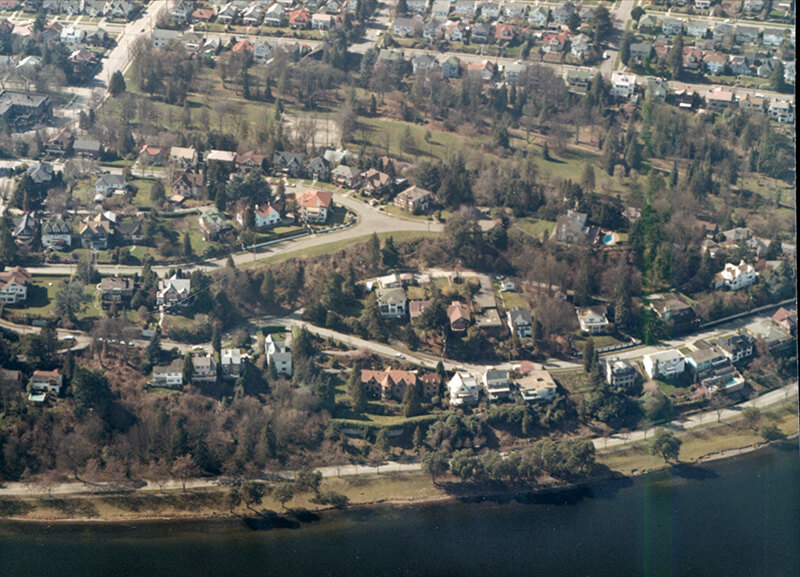
After being interrupted for a number of blocks by Interstate 90, S Atlantic Street reappears at 21st Avenue S and goes a block to just east of 22nd Avenue S. (Here, it gives its name to the surrounding Atlantic neighborhood.) It resumes — again having been interrupted by Interstate 90’s Mount Baker Tunnel — at Bradner Place S and goes ⅓ of a mile east to Lake Washington Boulevard S, the portions between 30th Avenue S and 31st Avenue South as well as between 32nd Avenue S and 33rd Avenue S being stairways. The right-of-way begins again at 35th Avenue S and goes around ⅛ of a mile east to Lake Washington, but is either incorporated into adjacent homeowners’ yards or serves as their driveways for most of this distance. Between Lakeside Avenue S and the water, it is one of the city’s shoreline street ends.

Born and raised in Seattle, Benjamin Donguk Lukoff had his interest in local history kindled at the age of six, when his father bought him settler granddaughter Sophie Frye Bass’s Pig-Tail Days in Old Seattle at the gift shop of the Museum of History and Industry. He studied English, Russian, and linguistics at the University of Washington, and went on to earn his master’s in English linguistics from University College London. His book of rephotography, Seattle Then and Now, was published in 2010. An updated version came out in 2015.