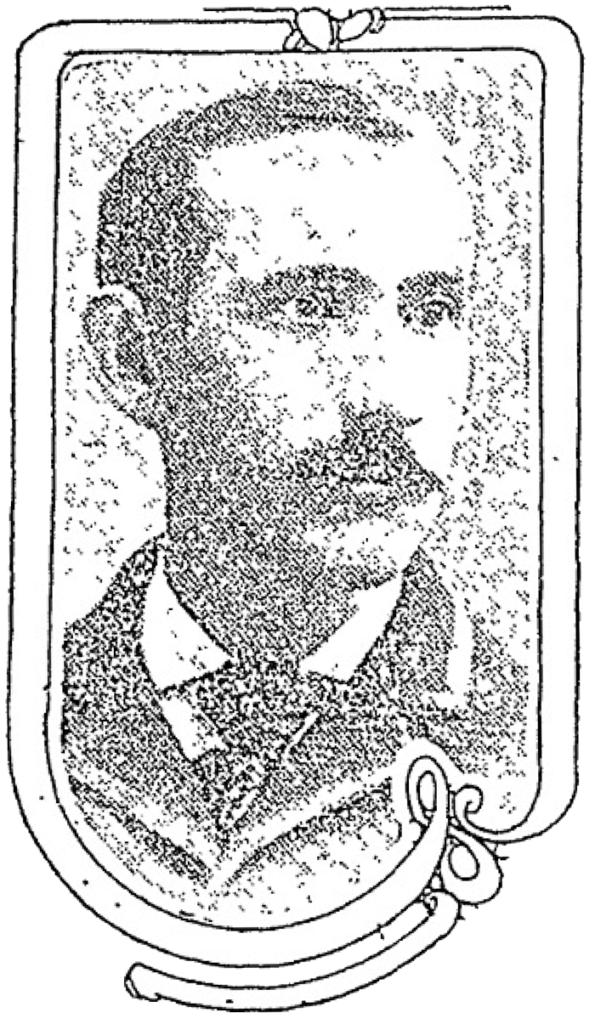
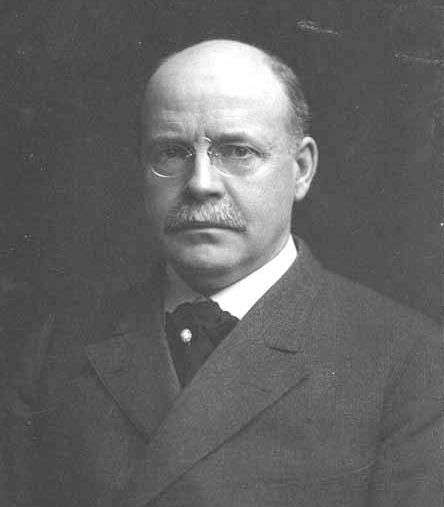This street was created in 1882 as part of Latta’s Addition to the City of Seattle, filed by Marion Cline Latta (1845–1924) and his wife, Mary (1867–1929). An architect, carpenter, and builder by trade, he came to Seattle in 1875 and left for what is now Bellingham in 1883; between then and 1918 he held various political offices, including city councilman, school board director, mayor, county commissioner, city treasurer, and city street superintendent.
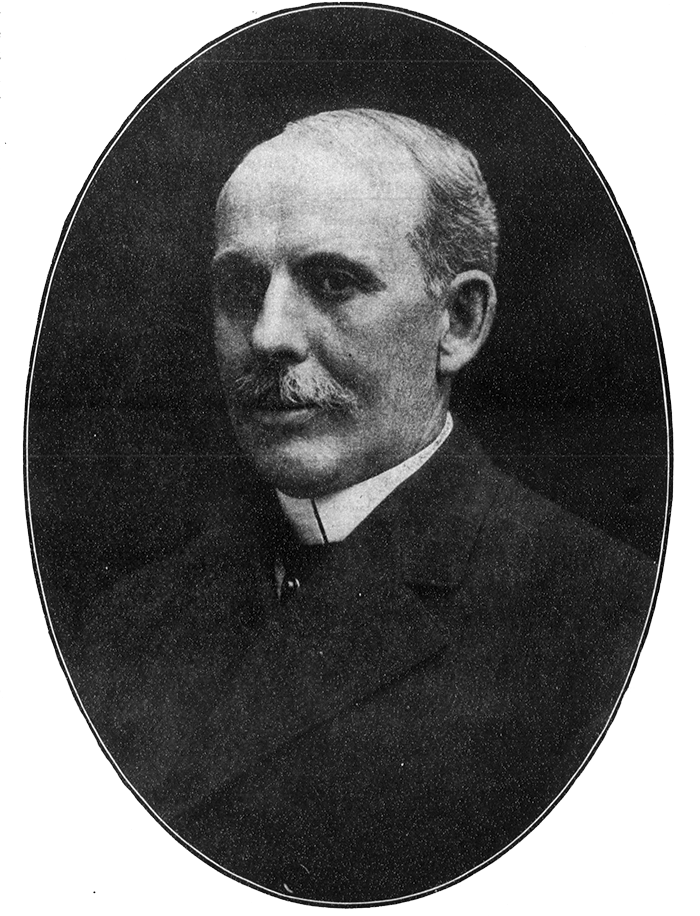
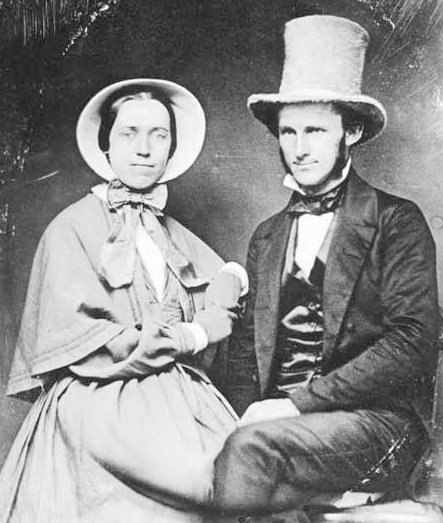
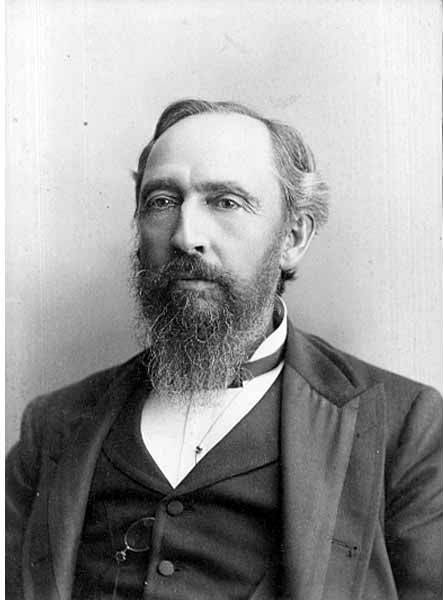
In that plat, Orange Avenue, as it was then named, is to the east of Jacobs Avenue, which is today Warren Avenue N. When I first saw this, I immediately thought of Orange Jacobs (1827–1914), associate, then chief justice of the territorial supreme court from 1869 to 1875, territorial delegate to Congress from 1875 to 1879, mayor of Seattle from 1879 to 1880, territorial councilman from 1885 to 1887, city attorney in 1890, and superior court judge from 1896 to 1900.
I have no proof, of course, that Orange Avenue was named for Orange Jacobs — people rarely, if ever, documented why they gave particular names to streets in their subdivisions — but Jacobs and Latta were both Republicans and, more importantly, members of the same Masonic lodge, so for now I’m willing to put Jacobs down as the namesake of Orange Place N.

Born and raised in Seattle, Benjamin Donguk Lukoff had his interest in local history kindled at the age of six, when his father bought him settler granddaughter Sophie Frye Bass’s Pig-Tail Days in Old Seattle at the gift shop of the Museum of History and Industry. He studied English, Russian, and linguistics at the University of Washington, and went on to earn his master’s in English linguistics from University College London. His book of rephotography, Seattle Then and Now, was published in 2010. An updated version came out in 2015.