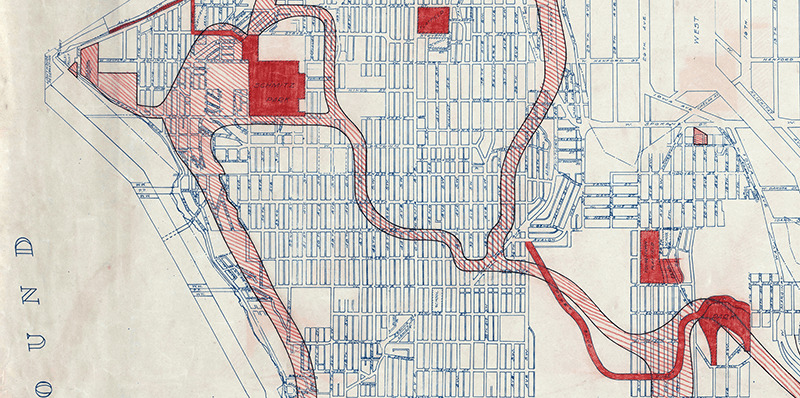
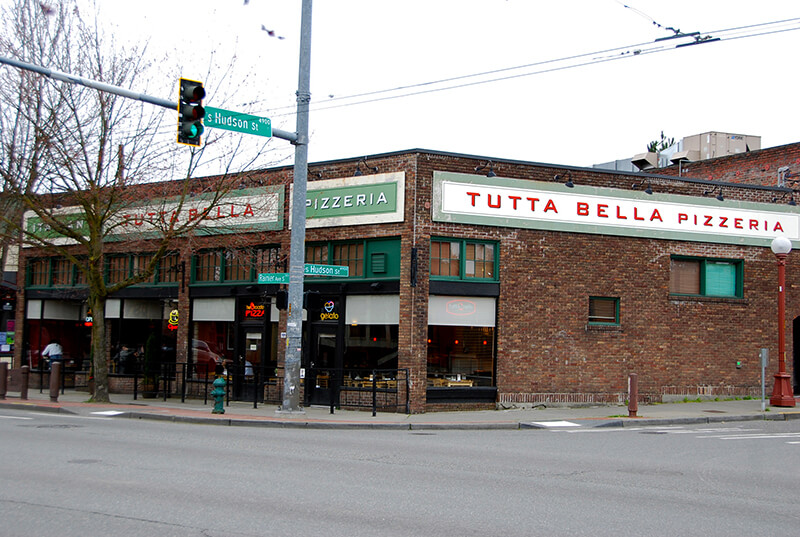
This street was created in 1891 as part of the plat of Columbia, which incorporated in 1893 and was annexed to Seattle in 1907, becoming the neighborhood of Columbia City. Part of a series of streets named after explorers — (Christopher) Columbus Street (subsequently changed to Edmunds Street), Ferdinand (Magellan) Street, and Americus (Vespucci) Street — it was named for English explorer Henry Hudson (c. 1565–disappeared 1611), namesake of Hudson Bay in Canada and the Hudson River in New York and New Jersey.
After a false start as a dead-end road west of 57th Avenue S, S Hudson Street begins at 53rd Avenue S and goes ⅓ of a mile west to 47th Avenue S, becoming a stairway between 50th Avenue S and 49th Avenue S. It resumes at 46th Avenue S and goes ¾ of a mile west to Martin Luther King Jr. Way S. After another couple of short segments, it begins again at 28th Avenue S and goes ¼ mile west to 24th Avenue S. There are two more short segments on Beacon Hill, and then Hudson Street resumes in Georgetown, going ⅖ of a mile from 4th Avenue S to E Marginal Way S.
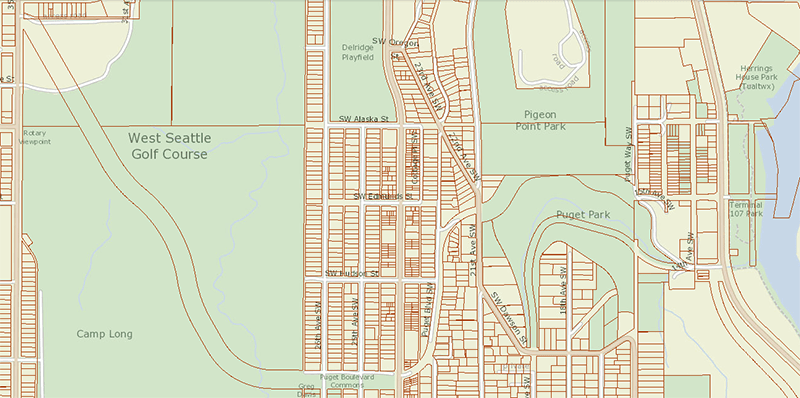
In West Seattle, SW Hudson Street begins as a service road and footpath within Puget Park off 18th Avenue SW. Its first appearance as a residential street is at Puget Boulevard SW, where it goes ⅕ of a mile to the West Seattle Golf Course. It then picks up again at 35th Avenue SW, where it goes just over a mile to SW Jacobsen Road, becoming a stairway three separate times along the way.

Born and raised in Seattle, Benjamin Donguk Lukoff had his interest in local history kindled at the age of six, when his father bought him settler granddaughter Sophie Frye Bass’s Pig-Tail Days in Old Seattle at the gift shop of the Museum of History and Industry. He studied English, Russian, and linguistics at the University of Washington, and went on to earn his master’s in English linguistics from University College London. His book of rephotography, Seattle Then and Now, was published in 2010. An updated version came out in 2015.